Utilizing such frameworks saves time and effort, allowing proposers to focus on content rather than formatting. These frameworks also enhance professionalism by presenting information in a clear, concise, and persuasive manner, increasing the likelihood of securing funding or approval. Standardized structures improve comparability across different proposals, simplifying the evaluation process for decision-makers.
This foundation allows for a deeper exploration of specific elements within proposal development, including best practices for articulating value propositions, tailoring content to specific audiences, and strategies for effective budget presentation.
Key Components of a Structured Proposition Framework
Effective frameworks for formal project or service propositions typically encompass several key components, each serving a specific purpose in conveying the value and feasibility of the proposed undertaking.
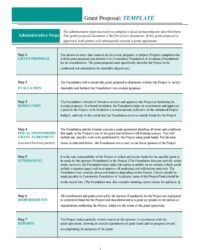
1: Executive Summary: A concise overview of the entire proposal, highlighting the key problem, proposed solution, and expected benefits. This section serves as a brief introduction for readers.
2: Problem Statement/Needs Assessment: A clear articulation of the challenge or opportunity being addressed. This section establishes the context and rationale for the proposed solution.
3: Proposed Solution: A detailed description of the proposed approach, methodology, and deliverables. This section outlines the specific actions to be taken and how they will address the identified problem.
4: Project Timeline/Implementation Plan: A schedule outlining key milestones and deadlines. This component demonstrates a clear understanding of project management and realistic expectations for completion.
5: Team/Qualifications: An overview of the individuals or organizations involved, highlighting relevant experience and expertise. This section establishes credibility and builds confidence in the proposer’s ability to deliver.
6: Budget/Cost Analysis: A detailed breakdown of projected costs, including personnel, resources, and materials. Transparency in financial planning is essential for building trust and securing approval.
7: Evaluation Plan: Metrics and methods for measuring the success and impact of the proposed project. This component demonstrates accountability and a commitment to delivering measurable results.
These elements combine to create a comprehensive and persuasive argument for investment or approval, enabling informed decision-making and facilitating successful project implementation.
How to Create a Structured Proposition Framework
Developing a reusable framework for crafting formal propositions involves a systematic approach to defining key sections and their respective content. This ensures consistency and completeness in all submitted documents.
1: Define the Purpose: Clearly articulate the objective of the framework. Is it intended for internal project proposals, grant applications, or client-facing sales documents? Specificity ensures relevance and practicality.
2: Identify Key Sections: Determine the essential components based on the intended audience and purpose. Standard sections include an executive summary, problem statement, proposed solution, timeline, team qualifications, budget, and evaluation plan. Context-specific sections can be added as needed.
3: Develop Content Guidelines: Establish clear guidelines for each section, specifying the type of information required, preferred formatting, and desired level of detail. This promotes consistency and clarity across all proposals.
4: Create a Template Document: Translate the defined sections and content guidelines into a tangible template document. Utilize formatting tools like headings, subheadings, bullet points, and tables to enhance readability and organization.
5: Test and Refine: Pilot the template with a small group of users and gather feedback. Identify areas for improvement in terms of clarity, usability, and effectiveness. Iterative refinement ensures a practical and user-friendly tool.
6: Implement and Train: Introduce the finalized template to all relevant stakeholders and provide training on its proper usage. Ongoing support and periodic reviews maintain its effectiveness and relevance.
A well-defined framework streamlines the proposal development process, ensures consistency in messaging, and increases the likelihood of securing desired outcomes. Regular review and adaptation maintain its efficacy in a dynamic environment.
Standardized structures for developing project or service propositions offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency, clarity, and persuasiveness. From providing a consistent framework for presenting essential information to streamlining the evaluation process for decision-makers, leveraging these pre-designed formats contributes significantly to successful outcomes. Key components such as executive summaries, problem statements, proposed solutions, timelines, team qualifications, budgets, and evaluation plans ensure comprehensive and compelling narratives. Methodical creation and implementation of these frameworks, involving clear definition of purpose, identification of key sections, development of content guidelines, template creation, testing, and refinement, lead to effective tools that support consistent messaging and improve the probability of securing approvals and funding.
Ultimately, the strategic adoption and consistent utilization of these structured frameworks represent an investment in clear communication and effective project management, contributing significantly to organizational success in a competitive landscape. Adaptability and continuous improvement of these tools remain crucial for maintaining their relevance and maximizing their impact in evolving environments.