Utilizing such a structure offers several advantages. It streamlines the application process, saving time and effort for both applicants and reviewers. A well-designed framework helps ensure clarity and consistency, making it easier for funders to assess proposals and compare them fairly. Furthermore, these resources can guide applicants in articulating their project’s value and demonstrating its alignment with the funder’s priorities, improving the chances of securing funding.
This article will delve further into the essential components of these valuable resources, offering practical guidance on how to effectively utilize them to develop successful funding requests.
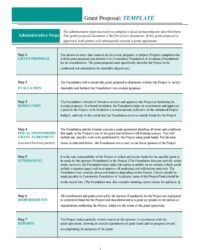
Key Components of a Typical Funding Request Structure
Effective requests for funding share common structural elements. Understanding these components is crucial for developing a competitive submission.
1. Executive Summary: This concise overview provides a compelling snapshot of the project, highlighting its purpose, key activities, and anticipated outcomes. It should capture the funder’s attention and create interest in learning more.
2. Need Statement: This section articulates the specific community need or problem the project addresses. It should clearly explain the issue, its impact, and why it requires funding.
3. Project Description: This detailed explanation outlines the project’s goals, objectives, and activities. It should describe how the project will address the identified need and the expected results.
4. Budget: A detailed budget outlines all projected expenses, demonstrating how the requested funds will be used. It should be clear, realistic, and justified in relation to the project activities.
5. Timeline: This section presents a clear schedule for project implementation, including key milestones and deadlines. It demonstrates the project’s feasibility and provides a roadmap for progress monitoring.
6. Evaluation Plan: This component outlines how the project’s success will be measured. It should describe the metrics and methods that will be used to track progress and demonstrate impact.
7. Organizational Background: This section provides information about the applying organization, including its mission, history, and relevant experience. It establishes credibility and demonstrates capacity to manage the project effectively.
8. Sustainability Plan (Optional): For projects intended to have long-term impact, a sustainability plan outlines strategies for maintaining the project beyond the initial funding period. This might include plans for securing additional funding or building community partnerships.
By incorporating these components, applicants can construct well-structured, persuasive submissions that effectively communicate the value and potential of their projects.
How to Create a Structure for Funding Requests
Developing a standardized structure for community project funding requests involves careful planning and consideration of key elements. A well-designed template ensures consistency and clarity, facilitating both application creation and review processes.
1. Define the Purpose: Clarify the specific goals and objectives the structure aims to achieve. Determine which types of projects it will support and the information required for effective evaluation.
2. Identify Essential Components: Determine the necessary sections based on typical funder requirements. These often include an executive summary, need statement, project description, budget, timeline, evaluation plan, and organizational background. Consider optional sections like a sustainability plan.
3. Develop Clear Instructions: Provide concise and unambiguous guidance for completing each section. Explain the purpose of each component and offer examples of effective responses.
4. Establish Formatting Guidelines: Specify formatting requirements, such as font size, margins, and page limits. Consistent formatting enhances readability and professionalism.
5. Incorporate Accessibility Features: Ensure the structure is accessible to individuals with disabilities. This may involve providing alternative formats or using accessible design principles.
6. Pilot Test and Refine: Before widespread implementation, test the structure with a small group of users. Gather feedback and make revisions based on their experiences.
7. Disseminate and Train: Once finalized, distribute the structure widely and provide training on its effective use. Offer ongoing support and answer questions as needed.
A well-crafted structure provides a valuable tool for both applicants and funders. It streamlines the application process, promotes clarity and consistency, and ultimately increases the likelihood of successful community projects.
Standardized structures for requesting funding provide a crucial framework for securing resources for community projects. These frameworks streamline the application process, ensuring applicants address all necessary information while enabling funders to evaluate proposals efficiently and fairly. By understanding the key componentsexecutive summary, need statement, project description, budget, timeline, evaluation plan, and organizational backgroundand following best practices for development, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to articulate project value and secure essential funding.
Effective utilization of these structured formats empowers communities to access the financial resources necessary to address critical needs and drive positive change. Investing time and effort in crafting well-structured, compelling applications strengthens the likelihood of project success, leading to tangible improvements in community well-being and fostering a more vibrant and resilient future.